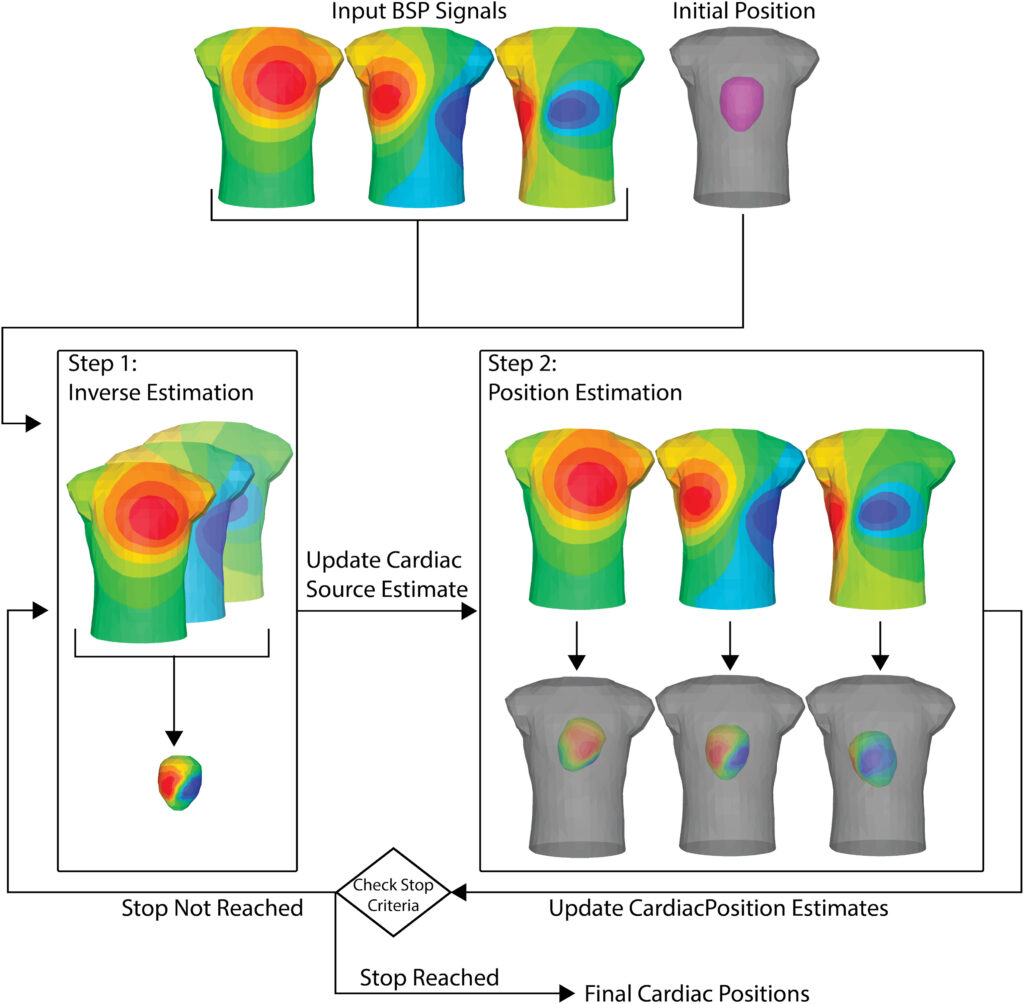
Body Surface Recordings Can be Used to Identify the Position of the Heart
In this study we demonstrated a novel optimization strategy to identify the position of the heart within the chest using recordings from the body surface alone. This method leverages the relative differences in body surface ECG maps between heart beats to optimize the position of the heart for each heartbeat. Our novel method leverages the forward and inverse relationship between body surface potentials and cardiac bioelectric sources which is a key aspect of electrocardiographic imaging (ECGI). The figure depicts the overall algorithm. During step 1, body surface potentials from multiple heart beats with multiple different assumed cardiac positions are used to estimate a single inverse solution (estimation off the cardiac sources that gave rise to all of these body surface potentials). Then, in step 2 the estimated inverse solutions are used to update an estimate of the cardiac position by minimizing the error between the forward solution to the torso surface and the measured body surface potentials. These processes are repeated until residual error is acceptably low or another stop criteria is reached, yielding an estimate of the cardiac position for each heart beat as well as the final inverse solution.
Jake A. Bergquist, Jaume Coll-Font, Brian Zenger, Lindsay C. Rupp, Wilson W. Good, Dana H. Brooks, Rob S. MacLeod, Reconstruction of cardiac position using body surface potentials, Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.105174

